Top 4 Benefits of Strength Training with Free Weights + Recommended Exercises
Strength training is like a magic potion for your body. It not only transforms your physique but also brings a host of benefits that go beyond just looking good. One of the most effective ways to engage in strength training is by using free weights. In this article, we’ll explore the top four benefits of strength training with free weights and highlight six of the best exercises to get you started on your journey to becoming a stronger, healthier you!
1) Building Functional Strength:
One of the key benefits of strength training with free weights is the ability to build functional strength. Unlike machines that isolate specific muscles, free weights require the engagement of multiple muscle groups to stabilize and control the weight. This mimics real-life movements, making your muscles work together as a cohesive unit. Compound exercises like squats, deadlifts, and lunges are excellent choices for developing functional strength using free weights.
Recommended Exercises:
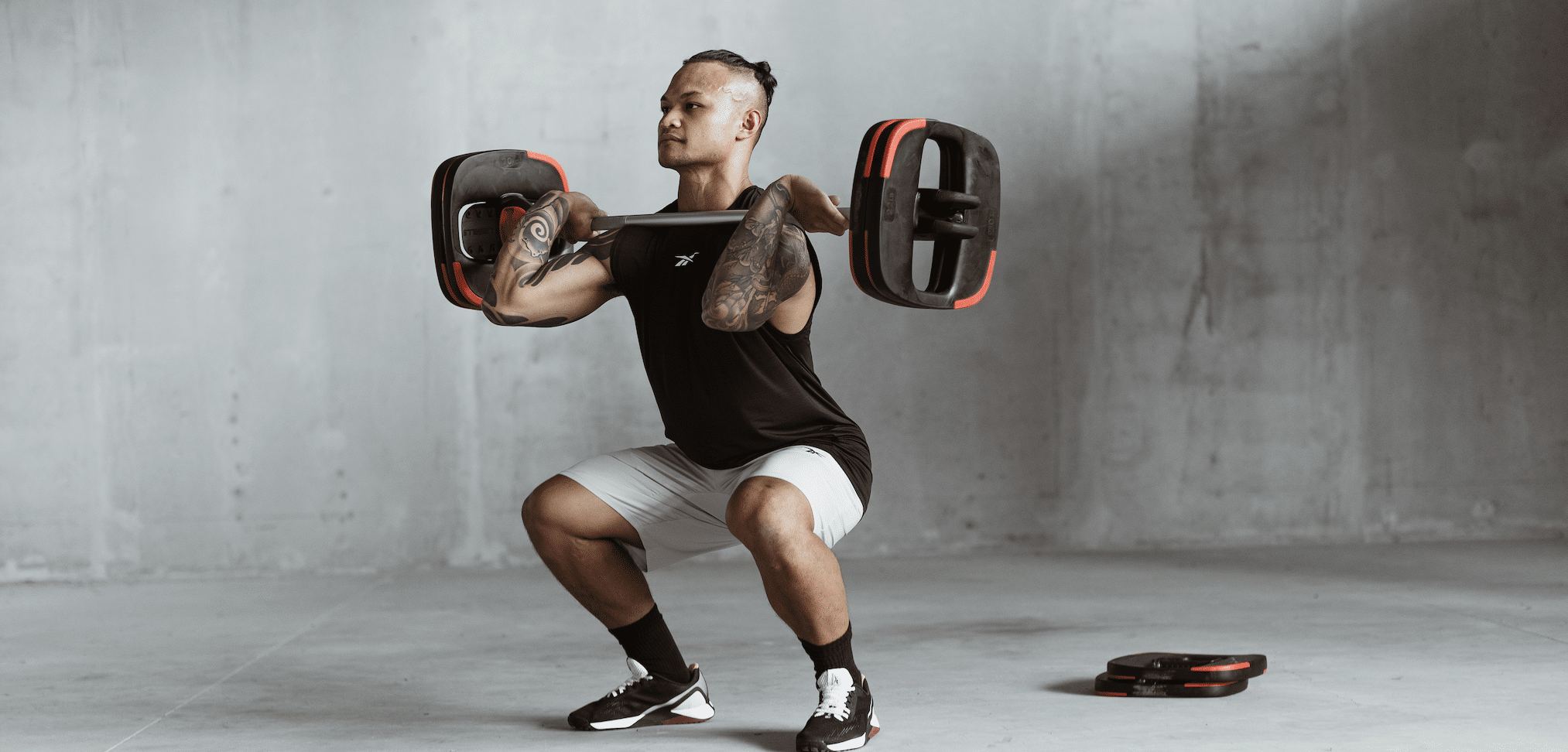

Barbell Squats
Targets the lower body, particularly the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes.
- Keep your chest lifted and maintain a neutral spine throughout the movement.
- Engage your core and keep your abdominal muscles tight to support your lower back.
- Ensure your knees track in line with your toes to avoid unnecessary stress on the joints.
- Drive through your heels as you push up to maintain balance and engage the proper muscles.
Barbell Deadlifts
Engages the posterior chain, including the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back.
- Engage Your Core: Prioritize core engagement throughout the movement. Brace your abdominal muscles as if preparing to receive a punch. This helps stabilize your spine and protect your lower back during the lift.
- Keep the Bar Close: Maintain a close proximity between the barbell and your body throughout the entire movement. This promotes better balance and minimizes the strain on your lower back. The bar should essentially graze your shins as you lift.
- Hinge from the Hips: Initiate the movement by hinging from your hips, rather than squatting down. This allows you to maximize the involvement of your posterior chain muscles (hamstrings, glutes, and lower back). Keep your chest up and maintain a straight back as you lower down and lift the barbell.

Dumbbell Lunges
Works the lower body muscles, including the quadriceps, glutes, and calves.
- Maintain Proper Alignment: As you perform the dumbbell lunge, it’s important to maintain proper alignment throughout the movement. Keep these points in mind:
- Step forward with one leg, ensuring that your knee is directly above your ankle and not extending past your toes.
- Keep your torso upright, with your chest lifted and shoulders back.
- Engage your core muscles to maintain stability and prevent excessive leaning or tilting.
- Take a Long Enough Step: When stepping forward into the lunge, make sure to take a long enough step so that both your front and back knees are at approximately 90-degree angles when in the bottom position of the lunge. This helps ensure proper form and optimal activation of the leg muscles.
- Focus on Controlled Movements: Throughout the exercise, focus on controlled movements rather than rushing through the lunges. This allows you to maintain balance, stability, and better muscle engagement. Control both the lowering phase (eccentric) and the rising phase (concentric) of the lunge, emphasizing proper form and technique.
2) Increased Muscle Mass and Definition:
Strength training with free weights is a tried-and-true method for building muscle mass and achieving a sculpted physique. By subjecting your muscles to resistance, free weights stimulate muscle fibers to grow and adapt. Compound exercises like bench presses, shoulder presses, and rows target multiple muscle groups simultaneously, leading to overall muscle development and increased definition.
Recommended Exercises:
Barbell Bench Press
Targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps, contributing to a well-rounded upper body.
- Set Up Properly: Before you begin the exercise, ensure you have set up properly for the barbell bench press. Here are a few key points to remember:
- Lie flat on the bench with your head, upper back, and buttocks in contact with the bench.
- Position your feet firmly on the ground, creating a stable base.
- Grip the barbell slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, with your hands positioned evenly on the bar.
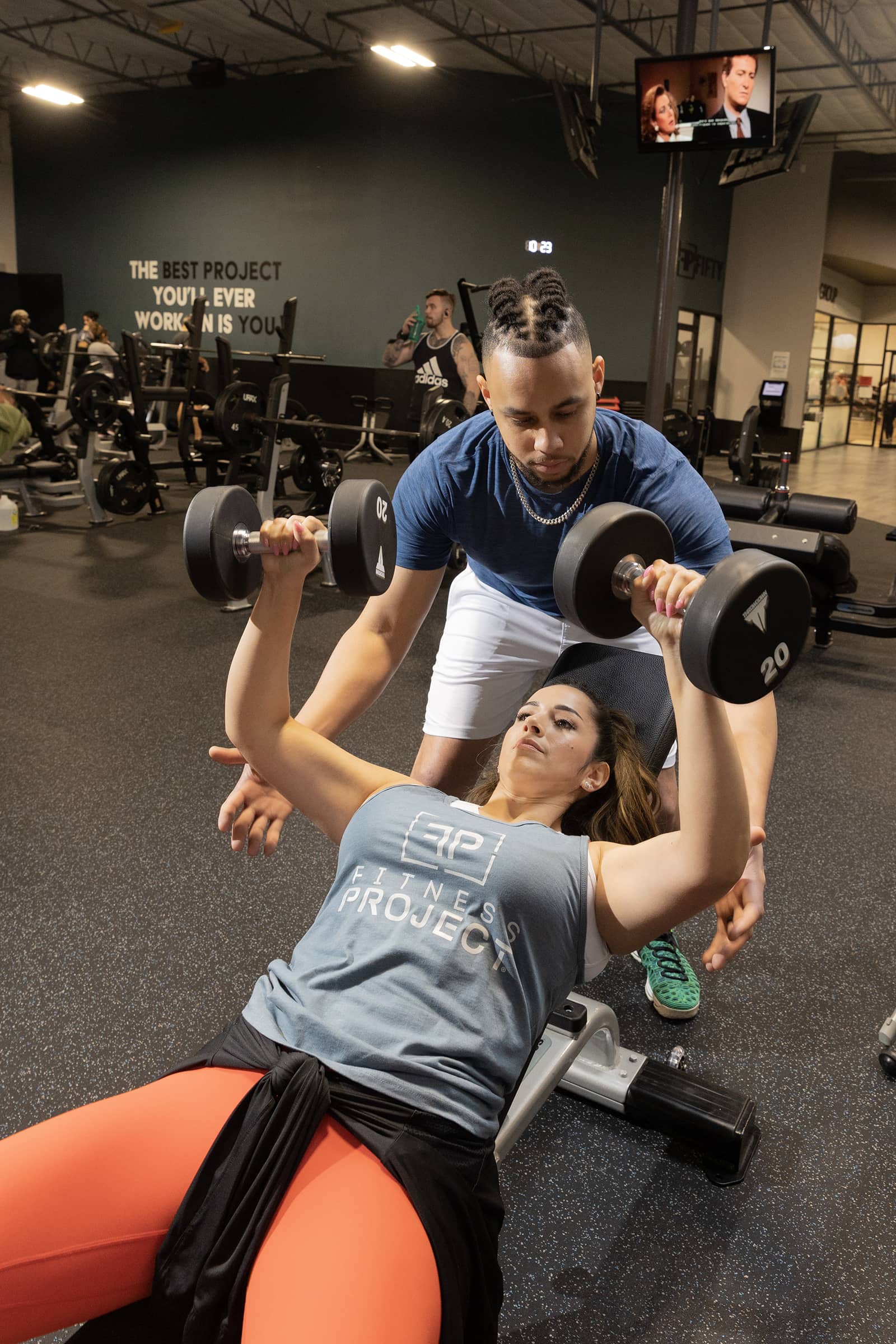
- Maintain Proper Form:
- Keep your chest lifted throughout the movement, allowing your shoulder blades to retract and creating a stable base of support.
- Lower the barbell under control until it lightly touches your chest, just below your nipple line. Avoid bouncing the bar off your chest.
- Push the barbell back up in a smooth, controlled motion, fully extending your arms without locking out your elbows.
- Engage Your Muscles and Breathe:
- Engage your core muscles throughout the exercise, bracing your abdominal muscles to provide stability and support for your back.
- Take a deep breath before you lower the barbell to your chest and exhale as you push it back up. This technique helps stabilize your torso and provides additional strength during the lift.
Dumbbell Shoulder Press
Engages the deltoids, triceps, and upper back muscles, promoting shoulder stability and strength.
- Start with Proper Set-Up: Before you begin the exercise, ensure you have set up properly for the dumbbell shoulder press. Here are a few key points to remember:
- Sit on a bench with back support or stand with good posture, maintaining a straight spine.
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand at shoulder level, palms facing forward.
- Keep your feet shoulder-width apart for a stable base of support.
- Maintain Proper Form:
- Engage your core and keep your chest lifted throughout the movement. This helps maintain stability and prevents excessive leaning or arching of the back.
- Press the dumbbells directly overhead in a controlled manner, avoiding any excessive leaning backward or forward.
- Fully extend your arms without locking out your elbows at the top of the movement. Maintain control as you lower the dumbbells back down to shoulder level.
- Focus on Controlled Movements and Breathing:
- Perform the shoulder press with controlled movements, focusing on proper form and technique.
- Exhale as you press the dumbbells overhead and inhale as you lower them back down. Controlled breathing helps maintain stability and control throughout the exercise.
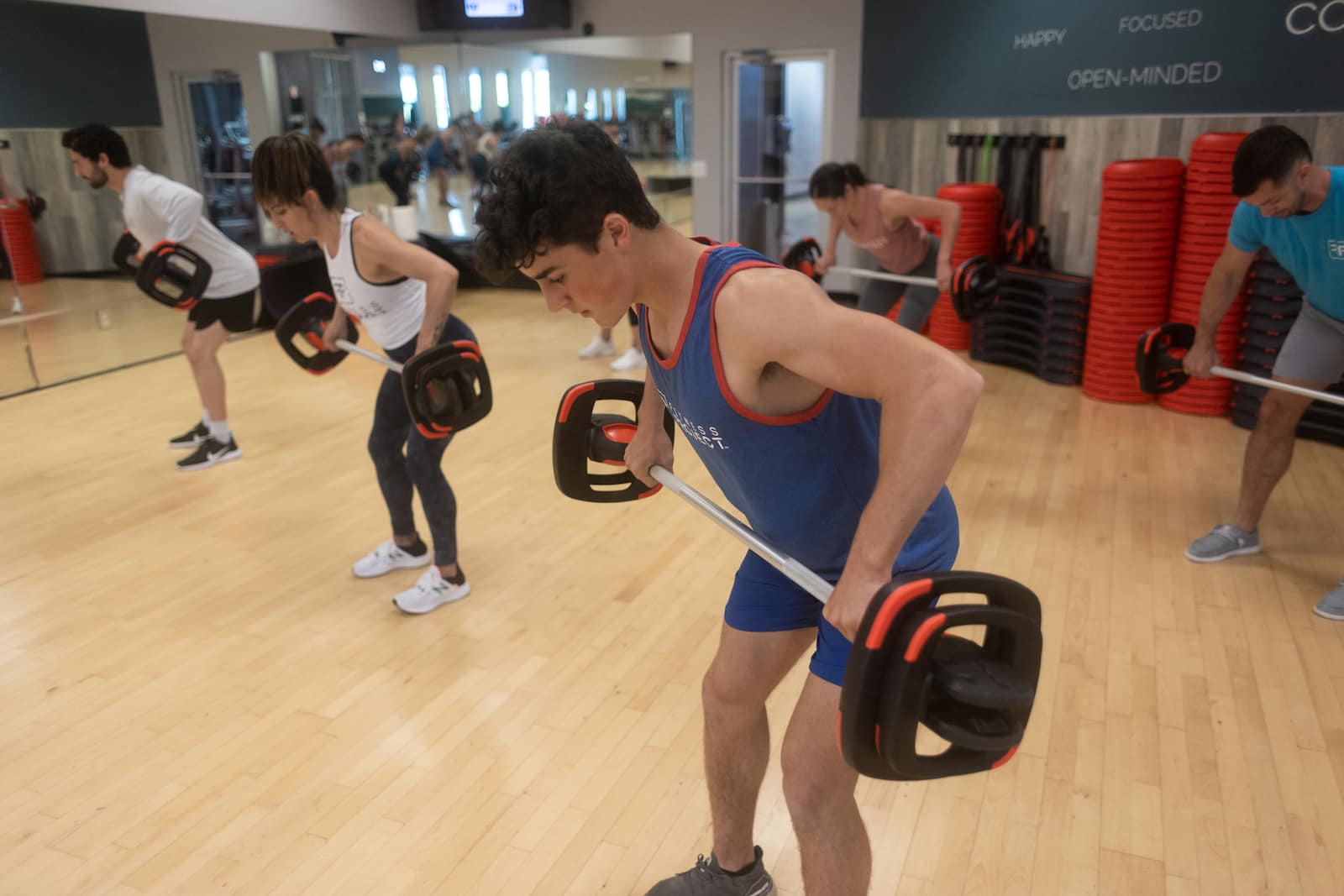

Bent-Over Rows
Works the muscles of the back, including the latissimus dorsi, rhomboids, and trapezius.
- Maintain a Strong and Stable Position:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart and knees slightly bent.
- Hinge forward at the hips, maintaining a flat back and a neutral spine.
- Engage your core muscles to provide stability and support throughout the exercise.
- Focus on Proper Form:
- Hold a barbell or dumbbells with an overhand grip, hands slightly wider than shoulder-width apart.
- Pull the weight towards your lower chest, squeezing your shoulder blades together.
- Keep your elbows close to your body as you lift, avoiding excessive swinging or using momentum.
- Control the Movement:
- Lower the weight in a controlled manner, allowing your arms to fully extend and maintaining tension in your back muscles.
- Avoid jerking or using excessive momentum during the lift.
- Control the weight as you bring it back up to the starting position, focusing on engaging the muscles of your back.
3) Improved Bone Density and Joint Health:
Strength training with free weights provides significant benefits beyond muscle growth. It also enhances bone density and joint health, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and age-related bone and joint issues. As you lift free weights, stress is placed on your bones, prompting them to adapt and become denser over time. This can help prevent injuries and improve overall mobility.
Recommended Exercises:

Barbell Overhead Press
Engages the shoulder and arm muscles while simultaneously promoting stability and strength in the shoulder joints.
- Set Up with Proper Form:
- Stand with your feet shoulder-width apart, ensuring a stable base.
- Grip the barbell with a slightly wider than shoulder-width grip, palms facing forward.
- Lift the barbell to shoulder level, resting it across your upper chest and shoulders.
- Maintain Good Posture and Alignment:
- Keep your chest lifted and your core engaged throughout the movement.
- Press the barbell directly overhead, ensuring your head stays aligned with your spine.
- Avoid leaning back excessively or arching your lower back, as this can strain your spine.
- Control the Movement:
- Exhale as you press the barbell overhead, engaging your core and using your shoulders and arms to drive the movement.
- Fully extend your arms at the top of the movement without locking out your elbows.
- In a controlled manner, lower the barbell back down to shoulder level, maintaining stability and control throughout the descent.

Dumbbell Step-Ups
Targets the lower body muscles, including the quadriceps, glutes, and calves, while also improving hip and knee joint stability.
- Step-Up with Stability:
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand, allowing your arms to hang naturally by your sides.
- Choose a sturdy bench or step that is approximately knee height.
- Step onto the bench with one foot, ensuring that your whole foot is placed firmly on the step.
- Press through your heel and engage your glutes and leg muscles to lift your body up onto the step.
- Maintain Good Posture and Control:
- Keep your torso upright throughout the movement, avoiding excessive leaning forward or backward.
- Engage your core muscles to maintain stability and control.
- Control the movement as you lift your body onto the step and avoid pushing off excessively with your other leg.
- Alternate Legs and Control the Descent:
- Step down from the bench by leading with the opposite foot, maintaining control and stability.
- Alternate the leading foot with each repetition to ensure balanced development.
- As you descend, lower your foot back down to the ground with control, focusing on engaging the muscles of the stepping leg.
4) Boosted Metabolism and Fat Burning:
Strength training with free weights is a fantastic way to rev up your metabolism and torch unwanted body fat. Unlike cardio exercises that primarily burn calories during the workout, strength training builds lean muscle mass, which increases your resting metabolic rate. This means you continue to burn calories even after your workout session is over, making weight management easier and more effective.
Recommended Exercises:

Kettlebell Swings
Engages the entire body, including the core, glutes, and legs, for a high-intensity fat-burning workout.
- Start with Proper Form and Technique:
- Stand with your feet slightly wider than shoulder-width apart, toes pointing slightly outward.
- Hold the kettlebell with both hands in an overhand grip, arms extended in front of you.
- Hinge at the hips, keeping your back straight and chest lifted.
- Initiate the swing by driving your hips forward explosively, using the power generated from your glutes and hamstrings.
- Focus on Hip Drive and Momentum:
- Use a powerful hip thrust to generate momentum, driving the kettlebell upward in a fluid motion.
- Allow the kettlebell to swing up to shoulder height, maintaining control and a straight line from your arms to your body.
- Avoid using your arms excessively to lift the kettlebell; the power should come from your lower body.
- Maintain Control and Core Engagement:
- Control the descent of the kettlebell by hinging at the hips and allowing it to swing back between your legs.
- Engage your core muscles throughout the movement to stabilize your torso and protect your lower back.
- Focus on maintaining a neutral spine, avoiding excessive arching or rounding.

Dumbbell Thrusters
Combines a squat and an overhead press, effectively targeting the lower body, core, and shoulders.
- Maintain Proper Form and Range of Motion:
- Hold a dumbbell in each hand at shoulder level, palms facing inward.
- Start with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Lower into a squat position by bending your knees and hips, keeping your chest up and maintaining a neutral spine.
- As you rise from the squat, simultaneously extend your legs and press the dumbbells overhead, fully extending your arms.
- Ensure that you achieve a full range of motion in both the squat and the overhead press.
- Engage Your Core and Breathe:
- Activate your core muscles by bracing your abdominals throughout the movement.
- Breathe in as you lower into the squat and exhale as you press the dumbbells overhead.
- Controlled breathing helps stabilize your torso and provides additional strength during the lift.
- Control the Movement and Use Proper Weight:
- Focus on controlled movements throughout the exercise, avoiding any jerking or rapid motions.
- Use an appropriate weight that allows you to maintain proper form and complete the full range of motion.
- Gradually increase the weight as you become more comfortable and confident with the exercise.
Strength training with free weights offers a plethora of benefits that go beyond the physical changes in your body. It builds functional strength, increases muscle mass, improves bone density and joint health, and boosts your metabolism for effective fat-burning. Remember to start with lighter weights and gradually increase the load as you progress. By incorporating the recommended exercises into your routine, you’ll be well on your way to achieving a stronger, healthier, and more confident you! So, grab those free weights and let the gains begin